NFT Meaning, What Exactly Are NFTs? A Thorough Guide


What is an NFT?
What Is The History of NFTs?
What Are The Attributes of An NFT?
What Are The Common NFT Standards?
What Are The Three Classes of People in the NFT Market?
What Can You Do With An NFT? What Are The NFT Use Cases?
Two Popular Concerns Related To NFTs
Is NFT A Scam? Why Are They so Controversial?
What is the Future of NFTs?
How To Create And Sell NFTs
On the 20th of January, 2022, Twitter announced a new feature where its iOS users can connect and display their NFTs as their profile pictures. This announcement made a lot of people, especially those who are not into tech, ask for the meaning of NFTs.
More people want to know why people spend millions of dollars on JPEGS, they want to know if NFTs have any tangible value beyond the current hype. However, some people have confessed that they are more confused about NFTs the more they read about them.
If you are in this shoe or you don't even have any idea of what NFTs are all about, then this blog post is for you. Don't feel odd. This piece will clear all the doubts you have about NFTs and also answer your questions.
One more thing, we will avoid blowing up blockchain jargon and communicate as clearly as possible. Let's dive in:
What is an NFT?
First of all, what does NFT stand for? Simply put, NFT stands for Non-fungible tokens. Yes, you might roll your eyes and wonder, "what is that supposed to mean?"
An NFT is a digital asset that represents real-world objects like art NFT, music NFT, in-game items, photography , meme NFT and videos
By "non-fungible," we mean that each NFT cannot be substituted for another. Each one is unique on the blockchain. By "token," we mean that NFTs are digital items or "things" on the blockchain.
Depending on the creator, NFTs can come in various forms and there are no bars to what cannot be tokenized. At the moment, NFTs can exist in these forms:
- Domain Names
- Memes
- Music
- Collectibles
- Artworks
- Tickets / cards
- Gaming
- Tangible Assets
The process of turning these digital files into NFTs is called minting. Before this time, NFTs are only minted on Opensea—which is on the Ethereum blockchain—but there are now other primary white label NFT marketplaces on other blockchains.

What Is The History of NFTs?
Although most people got to know about NFTs last year, they have existed way before then. According to research, one Kevin McCoy—now an Associate Professor of Art at the New York University—deployed the first NFT smart contract in 2014.
His NFT, which he named "Quantum," consisted of a video clip that he brought onto the Namecoin blockchain - which was an offshoot of the Bitcoin blockchain. McCoy says Quantum was a monetized graphics, and that was the beginning of NFTs.
While McCoy's "experimentation" may be applaudable, it's noteworthy that it had some inadequacies like having just 1 supply and some other technical issues.
But in the year 2015, we had a proper NFT project called Etheria which was built on the Ethereum blockchain. Although the Etheria NFTs were created more flawlessly, nobody showed interest in buying them. The expert opined now that it must have been due to poor marketing.

Fortunately, in 2021, NFTs caught the attention of everyone and the Etheria collection made a total revenue of almost $1.5 million. According to analytics, almost $41 billion was spent on NFTs in 2021.
This height of attention to NFTs in 2021 wouldn't have been possible without the prior existence of foundational NFTs projects like Cryptokitties, Cryptopunk, and the Bored Apes NFT community.
📌 Read more: NFT History Timeline —Journey of the foundation of the new digital economy
What Are The Attributes of An NFT?
Most NFTs around, especially Bored Apes and Cryptopunk, are always pixelated. This has misled most people to think only pixelated pictures are NFTs. This is not true.
Therefore, we would be taking a keener look at the attributes of an NFT, what are the features that make up an NFT? Or how can you successfully identify a digital item that is not an NFT?
Here are the attributes you must look out for in an NFT:
1. Scarcity and Rarity
The NFT market thrives on the law of demand and supply. While it is true that developers can order the minting of a lot of NFTs, they are programmed as little as they can. The rarer, the better.
Especially if the NFT is the one that suggests status and communal esteem, the core of its value is in its rarity. The reason the floor price of Bored Apes is currently trading at around $300k is that it has a limited supply of 10,000 pieces.
2. Transparency in Public blockchain
Non-fungible tokens should always be on the public blockchain where they can be used to interact with the ecosystem. This ensures transparency because all the activities relating to that NFT would be on distributed public ledgers.
This will make the buyers easily verify if the purported seller has a title to that NFT.
3. Unique Ownership
Each NFT is special. There are 10,000 pieces of identical NFT in the Lazy Lion NFT Collection, yet each of them is separate from the rest. The attribute of being special is the actual logic behind the term "non-fungible."
As a result, only one NFT wallet can host an NFT at a time. That is, only one person can own an NFT per time. The only possibility for different people to own an NFT is when they buy what we call fractional NFT.
4. Indivisibility and Indestructibility
With the current level of development, non-fungible tokens cannot be divided or broken into pieces. That is not how virtual items on the blockchain works. For example, NFT certificates must always be sent, received, and kept in full.
Similarly, one of the popular questions is, "Can NFTs be destroyed?" No, an NFT cannot be destroyed because it enjoys the security of the blockchain. The highest that can happen are only manipulations and not destruction.
What Are The Common NFT Standards?
If you have ever made crypto transactions before, you'd be familiar with various networks with which you can send them. This includes Solana, BEP20, BEP2, and ERC20.
There is a similar thing in NFT. The purpose of NFT standards is to identify the version it is compatible with and the features it would have.
Mainly, almost all NFT standards are Ethereum-based. Notwithstanding, other layer-2 networks that are compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine can interact and deploy NFT smart contracts in these standards.
These are the popular NFT standards:
1. ERC-721 Standard
The full meaning of ERC-721 is Ethereum Request for Comments 721. The trio of Jacob Evans, William Entriken, and a few other Ethereum developers proposed it in 2018 as the first standard for NFTs.
ERC-721 introduced the distinguishing factor of individual classes of tokens on the blockchain. Cryptokitties were the first set of NFT smart contracts that were deployed with this standard.
2. ERC-1155 Standard
The ERC-721 standard had a couple of downsides. It was slow, heavier to deploy, and data-consuming. Blockchain game developers were not comfortable with it. Hence the reason Enjin Devs created the ERC-1155 standard.
The ERC-1155 standard is built on the strength of both ERC-20 and ERC-721. The ERC-1155 introduced the facilitation of multi-token transactions. Simply put, the ERC-1155 made it possible to deploy fungible and non-fungible tokens in one smart contract.
3. ERC-809 Standard
This NFT smart contract standard is not as popular as the rest - at least, not yet. According to its GitHub documentation, ERC-809 enhances loanable tokens. In other words, it allows creators to rent out their NFTs.
Its staunch use case is in real-estate NFTs where realtors can rent their tokenized landed property. It's noteworthy that ERC-809 is in its nascent stage and it will have more utility ideas with time.
What Are The Three Classes of People in the NFT Market?

The NFT ecosystem has distinct players who are participating in the market for different reasons and perspectives. We will examine these three classes subsequently:
1. NFT Creators
Creators are at the core of the NFT ecosystem. Creators from all industries are contributing to the growth of NFT every day.
Who are NFT creators?
They are anyone who wishes to turn anything they own into digital proof of ownership. While most people often refer to artists and artists as those who can be NFT creators, the scope is wider than that.
You don't necessarily need to be art-related for you to be an NFT creator. The most important thing is for you to create a digital item on the blockchain.
For example, you can become an NFT creator by minting NFT certificates to your students.
2. NFT Buyers
Each artist has a particular set of people who resonate with his or her art. These people are ready to support such artists, appreciate them, and patronize their works. These are the buyers.
Apart from being a way of supporting, buying NFTs can give you access to some of your dream artists; being in their circles or communities.
If you want to buy some NFTs, these are the top NFT marketplaces:
- LooksRare
- OpenSea
- CryptoPunks
- Axie Infinity
- NBA Top Shot
- Mobox
📌 Read more: Who Actually Buys NFTs: A Deep Dive
3. NFT Traders
Some in the NFT space are not creators and they are more than mere buyers, these people are better classified as NFT traders or flippers. NFT traders buy and hold the NFTs that can go bullish soonest.
They sell these NFTs once their demand has skyrocketed and their floor prices have aced up. NFT trading has proven to be a profitable venture, hence the reason a lot of people are aping in.

What Can You Do With An NFT? What Are The NFT Use Cases?
Looking at the way people are spending thousands of dollars on NFTs, you might want to ask, "what can you do with an NFT? In what ways are NFTs useful at all?
In an actual sense, there is a lot that artists, creators, governments, and institutions can do with NFTs. This include
1 . Creative Sector
Players in the entertainment industry were pioneers of NFT adoption. First, it allows the celebrities—from the sports, music, and movie industries—to interact and benefit from their communities.
They can also sell NFT tickets to block frauds from entering the cinema without paying. With the coming of the Metaverse, more use cases of NFTs in the entertainment industry will keep showing up.
*An example of NFT Creator - Carl Cleanthes, Founder of Cleanthes Studios
2. Real Estate Tokenization
The current real estate industry has a couple of weaknesses including the problem of location, fractional ownership, and fundraising.
From the realtors' point of view, they can sell NFTs as a means to crowdfund the building of their property, thereby having more revenues to execute and complete their projects.
On the other hand, investors can now buy assets without the fear of regulatory hassles since the main owner can transfer the ownership through blockchain technology.
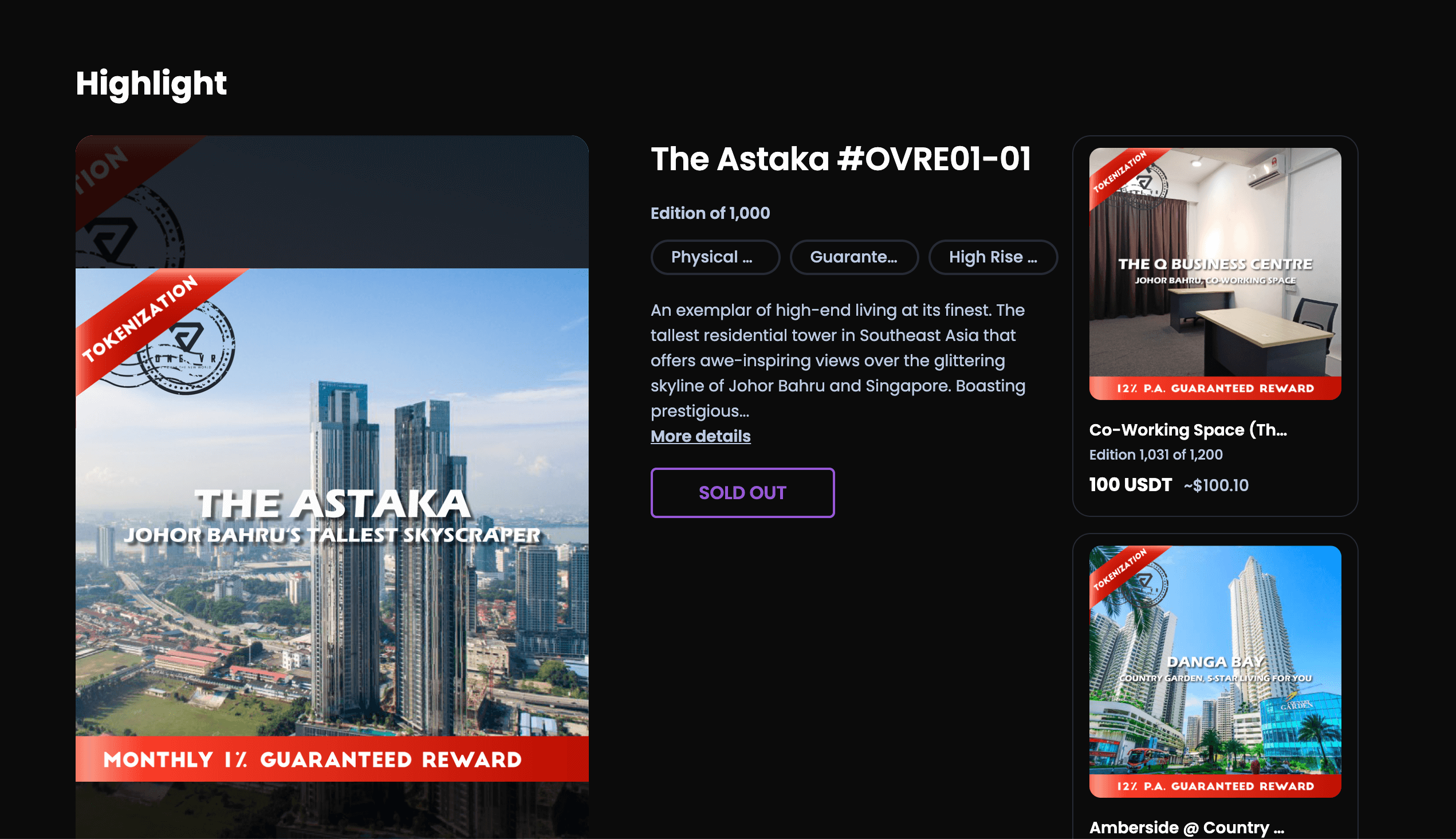
3. Medical Record Storage
The medical field will benefit a lot from NFTs. There have been cases where medical personnel mix up the results of one patient for another. Similarly, there are times confidential medical reports leak.
NFT will develop a secure means of storing medical data. The medical report of each patient can be minted and sent to his wallet address for maximal confidentiality.
Although no hospital has adopted this at the moment, it will become the order of the day with time.
4. Election with NFT voting system
Electioneering data can easily be manipulated. This is evident in the way people doctor voters' cards to vote more than once. Already, a couple of countries—like Ghana and India—are on track to implementing this.
Sierra Leone blazed the trail as the first country to carry out blockchain-based voting. Last year, one Rien Lewis Pecson—a 12-year old Philippine—built an NFT voting system.
The NFT voting system will usher in a transparent and immutable voting process.
The picture of the voting system that Rien built.

The picture of the voting system that Rien built.
5. NFT Helps To Protect IP Rights
According to Legal jobs, an average patent lawsuit costs almost $4 million for both parties. Meanwhile, there are other IP suits on Copyrights and Trademarks.
Non-fungible tokens are useful in maintaining and ascertaining authenticity. Musicians can sell their albums as NFTs, thereby blocking the possibility of making pirated copies.
📌 Read more: NFT Hype Officially Hit Vietnam As Binz Releases His Debut Music NFT Collection
Reports have it that the music industry loses almost $3 billion to pirates every year. Thus, NFTs are a dream come true for the creators' economy to have complete control of their crafts.
Two Popular Concerns Related To NFTs
As the NFT ecosystem is gradually evolving, two major issues are causing endless debates. A more viral adoption of NFT is predicated on the resolution of these debates.

1. NFT Royalties
Most creators and artists have expressed their pleasure in how royalties work in NFT.
Such that creators keep getting "kickbacks" once their NFTs are resold. This has helped the income of a lot of creators, and also gave people an avenue to support their favorite artists.
While NFT royalties may be favoring creators, it is not the case with the others who are also involved in the creation process. For example, only a musician gets NFT royalties, thereby excluding the producer who also contributed to the production.
Nonetheless, the current concerns of the proper distribution royalties in NFT is up because the ecosystem is still new. There are chances that this issue will be resolved in the future.
2. NFT Gas Fees
Perhaps the reason some couldn't ape into NFTs is because of the relatively high NFT gas fees. This mostly affects NFTs that are listed on the Ethereum blockchain. However, Ethereum Devs have been on track to tackle this exorbitant gas fee, and there have been plans to fork the network.
Fortunately, the popularity of the layer-2 solutions like Polygon, Arbitrum, and Optimism has made gas fees friendlier. With the look of things, it is possible that people will mint NFTs without paying gas fees in the future. Moralis has already created APIs and plug-ins for that.
📌 Read more: How to Integrate with Biconomy for gasless transactions
Is NFT A Scam? Why Are They so Controversial?
This is perhaps one of the most recurring questions about NFTs. Here is the logic of most critics:
- Group X, the early buyers of an NFT project, hypes the project.
- Group Y, the subsequent buyers, purchase the NFTs from X.
- Group X used Group Y as exit liquidity and dumps the NFT.
- The process continues ad infinitum till the value of the NFT may come back to zero.
Although the above logic may be the case with some NFT projects sometimes, it would be fallacious to call NFTs a scam as a whole. To be clear, it is not.
NFTs have a lot of practical use cases like storage of medical data, voter's cards, real-estate tokens, and so on. These utilities make it plain that NFTs are no scam.
In the same vein, there are a couple of reasons NFTs are so controversial.
First, only a few people understand how it works. That is understandable because new technologies often take time before being embraced.
Recall that only a few understood what the internet was about in the '90s. Thus, there will be less controversy about NFT once its education goes mainstream.
Secondly, there are arguments about its inimical climatic impact. This debate is being settled with the advent of eco-friendly blockchain networks like Algorand and Polygon.
What is the Future of NFTs?
While NFT-related news is appearing in almost every headline, some are concerned about its relevance in the future. Even a lot of NFT creators and traders are unsure about the extent to which NFTs will be useful in the next five decades.
First, the use cases—as discussed above—are beyond their impact on the creators' economy. It is only a matter of time before blockchain replaces Cloud as the most basic tech infrastructure.
At that time, NFTs will be the next big thing because almost every data on the blockchain would be in the form of NFTs.
Secondly, virtually every career path will find NFTs useful. This includes medicine, luxury, real estate, Development Operations, and even public policy.
There is more to NFTs than just the metadata, NFTs will be the future of community building, data, and infrastructure. However, it's noteworthy that these use cases would be appreciated and discovered one after the other.
How To Create And Sell NFTs
Since you now have a better understanding of NFTs, it's high time you created one on NFTify. NFTify is an NFT platform where you can display your crafts to millions of buyers.
Getting started on NFTify is as easy as integrating your domain and wallet address. In uploading your NFT, choose your preferred blockchain network and put it on the marketplace. We also have an import NFT collection feature where you can import and upload your NFTs in bulk.
See NFTify as a facilitator of your online NFT store, we provide you with in-built marketing tools to ensure that you generate revenues from your craft.
Knowing the role of content marketing in NFT marketing, we have added a blog feature for each of our customers. With your blog, you can write and post pieces of content that will drive traffic to your NFT store.
Having said that, you can collaborate with other artists on our platform. This will enhance your working together and the overall growth of your project.

with NFTify today
matter of hours, without a single line of
code or any upfront cost.
